
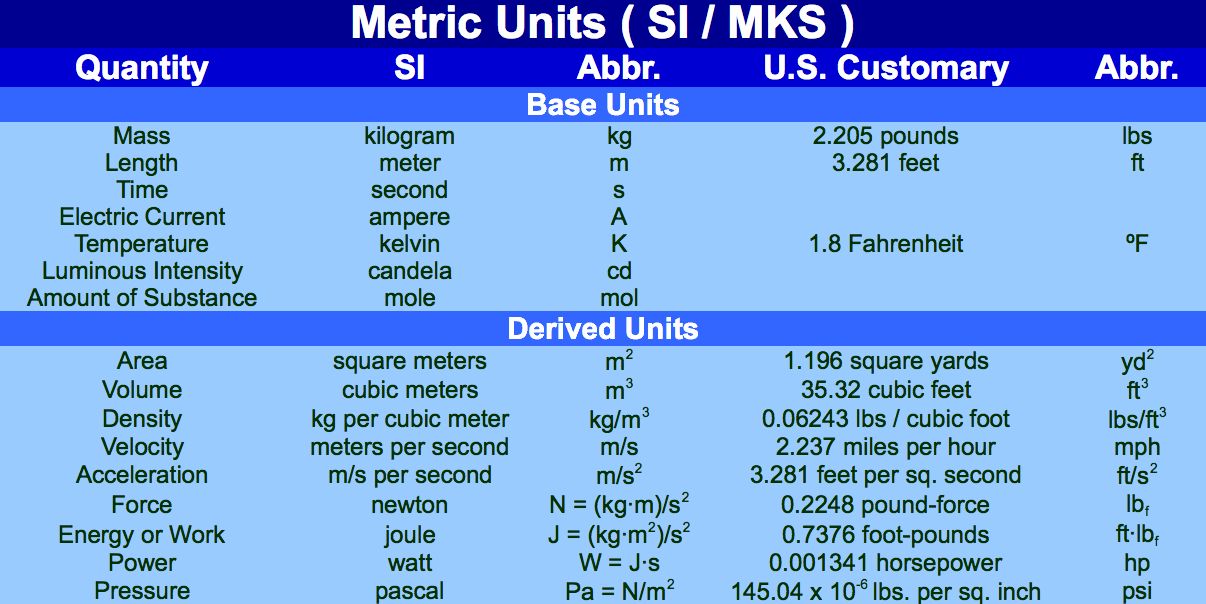

Using these two pieces of information, we can set up a dimensional analysis conversion.ĩ55\text Kilogram refers to 10 3 grams, while megagram refers to 10 6 grams. We will need two pieces of information from the table above. Let’s try converting 955 kilograms to megagrams. Here is an example of a one-step conversion between the SI system prefixes. Of course, you can always refer back to the tables above. Memorizing the different prefixes and their meanings makes it a lot easier to do these conversions, so try to memorize as many as you can. Name of unit, unit symbol, SI unit conversion factor. Interested in an Albert school license? Converting SI UnitsĬonverting between the different SI system prefixes is an essential science skill that requires practice. Magnetic Field Unit conversion Tool: Unit conversion of magnetic flux. For example, speed can be measured in meters per second, or in kilometers per nanosecond. The different base units can also be combined to form what are called derived units. Liter (L) is a special name for the cubic decimeter (dm 3). The SI unit of volume is the cubic meter (m 3), which is a derived unit. Instead, you would use kilometers or even megameters. Customary And Metric Units,customary Conversion,length Conversion Chart,si Units,math Educational Poster,classroom Wall Decorate Painting Calligraphy. Volume is the measure of the 3-dimensional space occupied by matter, or enclosed by a surface, measured in cubic units. For example, you wouldn’t measure the distance from LA to New York in meters, the base unit. These base SI units can be combined with any of the prefixes to create units that are most appropriate for what is being measured. Last, multiply the original expression of the physical value by the fraction, called a conversion factor, to obtain the same physical value expressed in terms of a different unit.These reference tables show the different bases and prefixes used to designate metric units with the SI system.Nominal values are sometimes allowed and used.ġ0 m i 1 h × 1609.344 m 1 m i × 1 h 3600 s = 4.4704 m s. It sometimes involves a slightly different configuration, or size substitution, of the item. It changes the measurement to convenient and workable numbers and units in the new system. It does not involve changing the physical configuration of the item being measured.īy contrast, a hard conversion or an adaptive conversion may not be exactly equivalent. This is sometimes called soft conversion. Customary to Metric Conversions Note: These approximate conversion factors are published as NIST SP 365, which is a laminated metric conversion card. Some conversions from one system of units to another need to be exact, without increasing or decreasing the precision of the first measurement. Mass (weight) Volume Temperature (exact) U.S. Historical definitions of the units and their derivatives used in old measurements e.g., international foot vs.The intended use of the measurement including the engineering tolerances.For example, since the inch was defined as the length corresponding to 2. The number of significant figures of the measurement. 3.785412 liters in other words, the inch-pound (customary) units are based on the SI units and multiplication or division is used to convert units from one system to another.The statistical confidence interval or tolerance interval of the initial measurement.The precision and accuracy of measurement and the associated uncertainty of measurement.Engineering judgment may include such factors as: This may be governed by regulation, contract, technical specifications or other published standards. Examples of the use of this table have already been given in. The process of conversion depends on the specific situation and the intended purpose. The table below gives conversion factors from a variety of units to the corresponding SI unit. Unit conversion is often easier within the metric or the SI than in others, due to the regular 10-base in all units and the prefixes that increase or decrease by 3 powers of 10 at a time. Conversion of units is the conversion between different units of measurement for the same quantity, typically through multiplicative conversion factors which change the measured quantity value without changing its effects.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
