
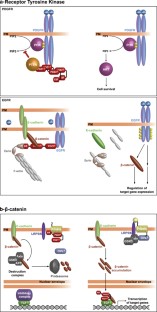
Principal mediator of signals emanating from the small GTPase RAS, thereby influencing multiple aspects of cell physiology
This pathway is composed of specific combinations of RAF, MEK, and ERK/MAPK isoforms and is one of the At leastįive groups of MAPK pathways have been distinguished in mammals, which include the extensively studied extracellular-regulated The prototypical MAPK pathway is a three-kinase module that transmits signals through a phosphorylation cascade. The evolutionarilyĬonserved mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways are among the best described examples (for review, see Schaeffer and Weber 1999). Suggest that KSR functions as a scaffold that assembles the RAF/MEK functional pair.Ĭells use a range of signaling pathways to convey distinct information to appropriate intracellular targets.

Lead to the formation of a RAF/MEK complex, thereby positioning RAF in close proximity to its substrate MEK. We further show that KSR associates independently with RAF and MEK, and that these interactions In agreement with this, we found that KSR facilitates Here, we show that KSR functions upstream of MEK within the ERK/MAPK module. In RAS-dependent genetic screens in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis elegans. One of these is Kinase Suppressor of Ras (KSR), a component previously identified Suspected to play critical roles in this process. Furthermore, the proposed compounds exhibited physicochemical and pharmacokinetics properties within the acceptable range for human usage, as anticipated by an in silico ADME study, making them lead molecules for developing new forms of medication.Mechanisms that regulate signal propagation through the ERK/MAPK pathway are still poorly understood. Flow cytometry and cell cycle assays revealed that apoptotic cell death induction occurred in the A549 cell line through the activation of certain caspases and the tumor suppressor P53 and through repressing the generation of BAX and PUMA. The designed molecules exhibited promising in situ cytotoxic activities, with IC 50 values ranging from 9.2 to 42.3 μM against MCF-7 and A549, comparable to 5-fluorouracil (which has IC 50 values of 10.32 and 5.8 μM against MCF-7 and A549, respectively) they also showed selective in vitro inhibitory activity against VEGFR2 when compared with other designed kinases, with compound 17 showing an IC 50 value (23 nM) as good as that of sorafenib (30 nM). In comparison to lenvatinib, which had a docking score of −12.47 kJ mol −1 and a Glide E-model value of −132.68 kcal mol −1, compound 17 had a decent docking score of −8.95 kJ mol −1 and a Glide E-model value of −92.17 kcal mol −1. Molecular docking studies demonstrated that most of the designed compounds bind VEGFR-2 adopting a DFG-in conformation, where the benzimidazole scaffold occupied the hinge region, the central aromatic ring occupied hydrophobic region I adjacent to the hinge region, and the hydrogen bond donor/acceptor bound to the hydrogen-bond-rich region. The expansion of the benzimidazole scaffold with heterocyclic rings resulted in a tridentate cyclic system that occupied the ATP-binding site and neighboring hydrophobic pocket, eliciting promising affinity and selectivity toward VEGFR2 through extra H-bonding and completely occupying the entrance region.
#Scaffold protein h1 series#
In the current study, a new series of benzimidazoimidazole, benzimidazothiazole, benzimidazotriazine, and benzimidazoquinazoline scaffolds was synthesized via C–H cycloamination, using a metal-free synthetic pathway, as potent antiproliferative antiangiogenic molecules against breast (MCF-7) and lung (A549) cancer cell lines. One of the current approaches used in drug discovery and development is the synthesis of novel small compounds from existing structural motifs via molecular hybridization.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
